Enormous Black Hole 33 billion times larger than Sun discovered, Scientists call it an extremely exciting
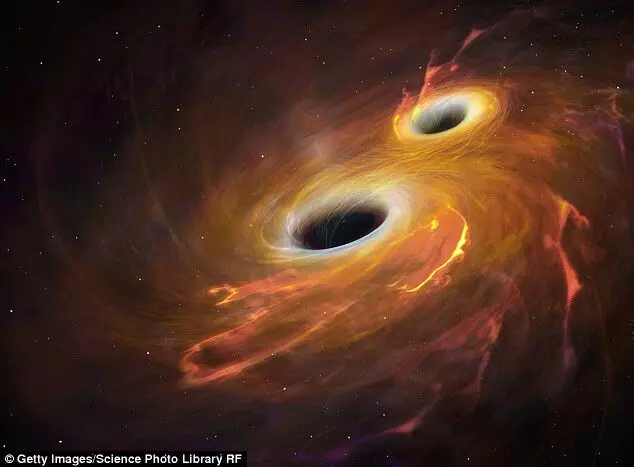
text_fieldsSpace scientists from Durham University in the UK have claimed to have discovered a supermassive black hole that is believed to be 33 billion times larger than the Sun.
According to the Metro, this is one of the largest black holes ever found, and its discovery has been reported in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. The news has been described as "extremely exciting" by the publication.
It is believed that similar massive black holes can be found at the centres of large galaxies, including the Milky Way, which is home to our solar system.
Reacting to the new discovery, lead author Dr James Nightingale, from the Department of Physics at Durham University said that the latest discovery of this particular black hole, which is assumed to be 33 billion times the mass of the Sun, is one of the largest ever detected and near the upper limit of how large we believe black holes can theoretically grow.
Scientists were able to discover this massive black hole through the use of gravitational lensing, which involves using a nearby galaxy to act as a giant magnifying glass.
Dr Nightingale explained that the majority of the largest known black holes are in an active state, in which matter that is drawn near to the black hole becomes heated and releases energy in the form of light, X-rays, and other radiation. However, through the use of gravitational lensing, it is possible to study inactive black holes, which is currently not feasible in faraway galaxies.
According to Metro, ultra-massive black holes are considered to be rare and difficult to detect, and their origins remain uncertain. Some experts suggest that they may have formed during the early stages of the universe when galaxies were merging with each other.